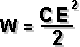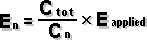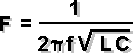Basic Electronics Formulas
| BASIC ELECTRIC CIRCUITS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
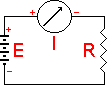
| OHM'S LAW
|
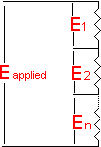
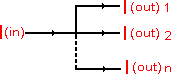
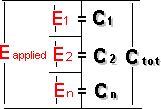
E(applied)=E1+E2+....En The current flowing toward a point in a circuit must equal the current flowing away from that point
I(in)=I(out)1+I(out)2+...I(out)n | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unknown Value | Formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| E | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| I | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| R | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
I = the current in amperes P = the power expressed in watts R = the risistance in ohms Resistance Circuit | Series Connected | Paralel Connected 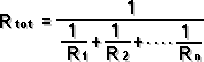 2 Paralel Connected Resistor | 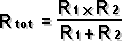 Capacitance Circuit | Paralel Plates | 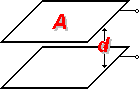 Charge Stored Energy Stored Paralel Connected | Series Connected 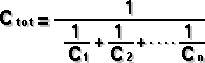 2 Series Connected 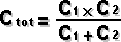
RC Time Constant | 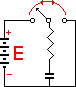 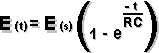
E(s) = potential of charging batteries in volts t = time in seconds e = natural logarithmic base = 2.718 R = resistance in ohm C = Capacitance in farads
T = time constant in seconds C = capacitance in farads R = resistance in ohm Inductance Circuit | Series connected | Paralel Connected 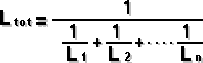 2 Paralel Connected Inductors | Mutual Inductance of 2 coils: |
the same unit as La and Lb La is the total inductance of l1 and l2 with fields aiding Lb = the total inductance of L1 and L1 with field opposing Coupling coeficient: | 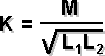
Reactance | Capacitive | 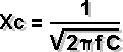
f = frequency in Hertz C= in Farad Inductive |
f = frequency in Hertz L = in Henry RESONANCE |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
Links
Updated January, 2004
![]()